Ketamine Explained
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic that is used both medically and recreationally, and it’s important to understand how it relates to drug testing, especially in occupational, forensic, and clinical settings. Here’s a detailed explanation tailored to the drug testing industry:
What is Ketamine?
-
Medical Use: Approved for anesthesia and more recently for treatment-resistant depression (as esketamine, under brand names like Spravato).
-
Recreational Use: Often used illicitly for its hallucinogenic and dissociative effects. Street names include “Special K,” “K,” or “KitKat.”
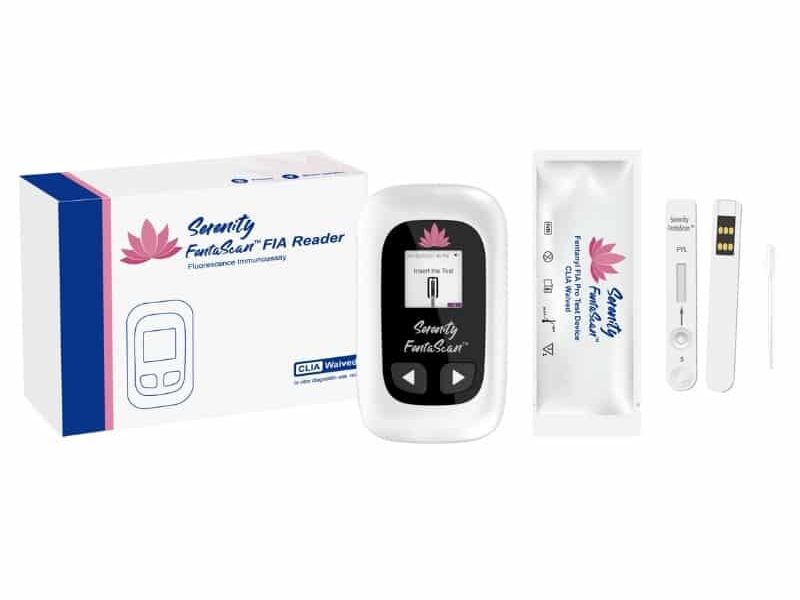
Detection of Ketamine in Drug Testing
Testing Methods
-
Immunoassay (Initial Screen): Most standard workplace drug panels (e.g., SAMHSA 5-panel) do not include ketamine by default.
-
GC-MS or LC-MS/MS (Confirmatory Tests): These sophisticated lab-based methods can specifically identify and quantify ketamine and its metabolites (e.g., norketamine).
Specimens Used
-
Urine (most common): Ketamine can be detected for up to 2–4 days after use.
-
Blood: Detection within 24 hours typically.
-
Hair: Can reveal use over a 90-day window.
-
Saliva: Less common for ketamine, but possible.
Relevance in Drug Testing Industry
1. Workplace Testing
-
Not routinely tested unless requested by the employer (e.g., for high-risk roles in aviation or healthcare).
-
May be included in expanded or customized drug panels.
2. Forensic and Legal Testing
-
Common in DUI or accident investigations, particularly if impaired driving is suspected and other drugs are not present.
-
Also relevant in sexual assault investigations, as ketamine is sometimes used as a “date rape” drug.
3. Clinical Toxicology
Challenges and Considerations
False Negatives in Routine Panels
Cost and Complexity
Regulatory Status
Emerging Trends
-
Increased medical use (e.g., esketamine) has raised concerns about therapeutic misuse.
-
Some drug testing services now offer ketamine-specific panels for clinics or employers concerned about dissociative abuse.
Summary
| Aspect |
Detail |
| Drug Class |
Dissociative anesthetic |
| Standard Testing Panel |
Not included by default |
| Detection Window |
1–4 days (urine); longer in hair |
| Confirmatory Testing |
GC-MS or LC-MS/MS |
| Common Uses |
Anesthesia, depression, recreational |
| Legal Status (US) |
Schedule III controlled substance |